WindowsFirewallRuleset
Security and privacy
This document provides suggestions and best practices on how to take control over your online privacy and how to maximize security of a personal computer.
Table of contents
- Security and privacy
The difference between security and privacy
Both security and privacy are important in the digital world.
Privacy refers to the control that you have over your personal information and how that information
is used.
Personal information is any information that can be used to determine your identity such as email,
credit card or bank details, home address, birthdate, geographical location etc.
Personal information may also refer to hardware ID’s, IP address, browsing habits etc. which if
gained access to may uniquely identify your system.
Security, on the other hand, refers to how your personal information is protected.
Security generally refers to the prevention of unauthorized access of data,
often involving protection against hackers or cyber criminals.
Security suggestions
In the following sections are most common security concerns and suggestions on how to deal with them.
Some security suggestions here also touch privacy but are more related to security.
Standard user account
Using standard (aka. non Administrative) Windows account for almost all use helps to guard your system because potential malware won’t be able to compromise system without you allowing such action by supplying your administrative credentials.
Administrative account is needed as well but it should be used for administration only.
The following site explains how to create standard user account:
Create a local user or administrator account in Windows
Digitally signed and trusted software
Installing and running only digitally signed software, and only those publishers you trust helps to ensure integrity of a system, because by running unsigned software you run the risk of installing malware or spyware.
Installing cracks, warez and similar is the most common way to let hackers in.
The following site explains How to verify Digital Signatures of programs in Windows
To enforce digital signature requirement for all software on your system follow steps below:
- Click start button
- Type:
secpol.msc - Right click on secpol.msc and click
Run as administrator - Expand node:
Security settings - Expand node:
Local policies - Expand node:
Security options - On the right find option
User Account Control: Only elevate executable files that are signed and validated - Double click it to open it
- Click on enabled checkbox and apply, click OK
Now if you attempt to install unsigned software an error will appear like in the image below:
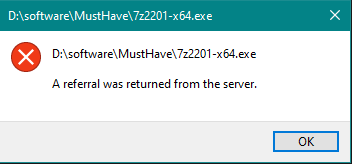
User Account Control
UAC helps mitigate the impact of malware by asking for consent prior to running an executable as
Administrator.
UAC has several protections levels, it’s recommended to set it to max, to configure UAC see:
Change User Access Control setting
See also:
UAC probably isn’t bulletproof though, you should be aware of Privilege escalation
Trusted and encrypted web sites
Visit only known trusted web sites, preferably HTTPS, and check links before clicking them.
Unencrypted web sites are subject to attack and the infomation you supply on such sites can end up
in wrong hands.
Also by visiting unknown or untrusted web sites you run the risk to connect to potentially malicious
web server or game server and similar.
To visit odd sites and freely click around do it in isolated browser session or virtual machine
Isolated or virtual session isolates your real system from isolated system in such a way where
interaction between the two is not possible by default.
This helps to prevent malware or an attacker gain access to your system or personal information.
How to configure isolated browser session depends on your web browser.
For MS Edge Chromium the following site explains how to get started:
Microsoft Edge support for Microsoft Defender Application Guard
If your browser does not support isolated browser session an alternative is to use virtual machine, however virtual machine consumes system resources since you would be running two systems at once.
The following site explains how to get started with Hyper-V virtual machine in Windows:
Install Hyper-V on Windows 10
Password manager
Use password manager capable of auto typing passwords and with the support of virtual keyboard.
Don’t use hardware keyboard to type passwords.
Your passwords should meet length and complexity requirements.
Never use same password to log in to multiple places, use unique password for each login.
Recommended password manager is Password Safe
More about the author of this program:
Schneier on Security - Password Safe
The significance of password manager autotype feature is that password doesn’t get copied to clipboard but instead goes directly from password manager into login form, thus avoiding the risk of potential malware stealing your password from the clipboard.
The benefit is also that you avoid potential keylogger since you won’t be using keyboard to type passwords.
The benefit is also you don’t have have to remember any passwords, so it’s easy to have complex and unique password for each site.
Email client and service
Don’t let your email client or web interface auto load email content.
Configure your mail client to be restrictive, also important not to open attachments or links in
mail you don’t recognize or didn’t ask for.
For recommended email service list see Privacy-Conscious Email Services
Suggested email service (from the list) is Proton mail
Antivirus and firewall
Never disable antivirus or firewall except to troubleshoot issues.
Troubleshooting doesn’t include installing software or visiting some web site.
Suggested anti virus is Windows defender
Suggested firewall is Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security
Of course with ruleset from this repository.
Web browser
Web browser is probably the most important thing of all described here since most of your online activity is by using the browser.
Protect your web browser maximum possible by restrictively adjusting settings, and avoid using addons except few which are known to be trusted by online community.
Suggested web browsers are subjective and it depends a lot on how much privacy is one willing to trade for speed, what matters most is to use the one which receives regular updates, most mainstream web browsers do.
Software updates
Keep your operating system, anti virus and web browser patched maximum possible, this means checking for updates on daily basis for these essential programs.
OS, AV and browsers are most essential to be up to date, but on regular basis you also want to update the rest of software on your computer, especially networking programs.
Separate account or computer
High value data, online purchases and financial transactions should be performed on separate computer or alternatively separate user account on same computer whose only purpose is to do this and nothing else, and to keep valueable data protected away from network.
Encryption
Encrypt your valueable hard drives or individual files, for computers or user accounts such as those which are used for special purposes like transactions or online purchases this is essential.
Suggested software for file and email encryption is Gpg4win
Suggested software for disk encryption is subjective.
Backup
Always keep a backup of everything on at least one drive that is offline and away from online machine.
If you have to bring it online, bring down the rest of network.
Suggested backup software is subjective, most secure method is external hard drive or separate computer.
Advanced Threat Protection
Advanced Threat Protection or ATP for short used to be a set of rules and settings which apply to business addition of Windows defender and pro edition of Windows, however these rules and settings can be applied on any system natively without any special paid software.
You can read more about this on the links below:
As already said good news is that you need none of these expensive software, in this repository in
Scripts\Security directory you’ll find the following scripts which automate these things as follows:
Deploy-ASRis used to deploy attack surface reduction rules on your systemSet-ATPis programatic way to configure Windows defender and enforce restrictive settingsShow-ASRis used to show settings applied byDeploy-ASRFind-UnsignedFileis used to detect unsigned software on your system and to perform automatic online malware analysis with VirusTotal for any unsigned file that is found, so that you don’t have to upload each file manually.
It’s recommended to take a look into these scripts to see what they do and how to use them before actually running them, you might want to adjust some of the settings according to your personal references.
Privacy suggestions
In the following sections are most common privacy concerns and suggestions on how to deal with them.
When it comes to privacy, briefly, there are two different defense categories:
-
Hide your online activity, is what people usually refer to when talking about “privacy”.
This relates to data such as hardware ID’s, browser fingerprinting, IP address etc. -
Prevent identity theft, refers to your personal information which could be used to identify you with the aim to perform things in your name.
This relates to data such as credit card number, home address, phone number etc.
VPN or proxy
When you connect to internet your computer is assigned a unique IP address, and likewise every other
computer or server on the internet has it’s own IP address, that’s how computers and servers
communicate over the internet.
By having someones IP a potential attacker can determine ones approximate geographical location as
well as scan their IP for vulnerabilities which can help to gain access to victim’s system.
One method how this is done is by using software such as nmap
VPN or proxy is used to hide your real IP from an endpoint to which you connect, such as a web
server or game server.
If somehow you end up on malicious server an attacker behind such a server might scan your IP to see
possibilities to compromise your system or privacy
By using VPN or proxy you do not connect directly to an endpoint but instead over VPN or proxy server.
By using VPN or proxy a potential attacker will have difficulty scanning your IP or determining your
location.
However VPN or proxy is not recommended for all scenarios and in some cases it may be dangerous,
for ex. connecting to your bank is better done directly because VPN or proxy server might as well be
malicious or there could be a bad employee working at VPN server watching for traffic going over VPN.
Another downsite to using VPN or proxy is that your internet connection will be slower.
One example where VPN is perfectly useful however is to avoid censorship, for example some sites might be restricted for your country, by using a proxy it would look as if you connect from some other country possibly not restricted and this would let you circumvent the restriction and access the site.
Another example where VPN or proxy proves useful is to avoid an IP ban.
However major benefit of using VPN or proxy is privacy because it helps to hide your online identity,
allowing you to browse the internet anonymously.
It’s difficult to suggest VPN since VPN’s aren’t free and proxy services which you can find online
aren’t to be trusted.
Suggested software for VPN or proxy that is free and open source is Psiphon,
github repo is here Psiphon-Inc/psiphon-windows
Psiphon is a standalone executable which doesn’t require elevation, it’s free, their company has servers world wide and you’re able to choose from a set of countries in the UI.
An alternative to Psiphon is Tor Browser which is open source project, there are
few pros and cons compared to psiphon, for ex. you might be unable to login to some sites from tor
network and might be presented with “anti robot” captcha often times.
Also you should be aware of exit nodes, in short don’t use tor for anything too personal, tor is
best for anonymous browsing and to browse deep and dark web.
DNS encryption
When you wish to connect to some server such as microsoft.com your computer needs to resolve
microsoft.com to an IP address which the computer understands.
You computer does this by contacting a DNS server such as google DNS, your computer then stores the
IP address into local cache so that it doesn’t need to contact DNS server again for subsequent
queries.
Your ISP (Internet Service Provider) or an intermediate attacker might watch over your DNS queries and harvest your browsing habits, which is a hit to privacy.
By using DNS encryption this can be prevented.
DNS encryption works by configuring computer to query DNS server which supports DNS encryption.
You only have to be careful to use DNS server which is trusted and one which provides maximum
security and privacy, this means servers which don’t collect logs and those which support DNSSEC.
DNS encryption is supported by some web browsers and even OS’s however not all have this functionality.
Suggested DNS encryption software is open source Simple DNSCrypt which is a UI frontend
for dnscrypt-proxy service and it ships with Simple DNSCrypt.
Browser extensions
Some browser extensions are essential for privacy, there are extensions which automatically handle cookies, hide adds, switch to HTTPS, prevent tracking and few other features which help to guard your online privacy.
You only need to ensure to use trusted extensions, preferably open source, those with positive reviews and those which hang around for long time.
Common recommendation is to minimize amount of extensions in your browser as much as possible,
because no matter how trusted an extension is you will have to allow it to access some of your data.
By minimizing the amount of extensions you reduce the risk or installing the wrong one.
Suggested browser extensions are:
Search engine
Which search engine you use matters for privacy but it also affects speed and quality of search
results.
google search is by far the best for good and fast search results but privacy wise it’s subject
to google privacy policy.
If you’re willing to trade speed for privacy consider privacy conscious search engine.
Common privacy mistakes
There are some privacy mistakes which we all did at least once.
-
First obvious privacy mistake is having just one email and using it for everything.
It is suggested to have three different emails as follows:-
One for personal real life use, which you share with institutional entities and your real life friends such as your bank or, your lawyer, your family, your relatives or paypal.
-
Second one for your regular online activity such as forums and web services which you regularly use.
-
And third one which is a “junk” mail which you use to register to unknown sites or services, sites which have poor or aggressive privacy policy or to register for a newsletter until you’re sure that the newsletter isn’t about spamming you or sharing your email with hostile services.
It’s also important that these email accounts aren’t registed at same email provider, some providers care more about your privacy than others, for your real life use the best one.
You should also take care of, in which country are email provider HQ’s located, for example swiss privacy laws are strict and more protective than those in the EU or the US, therefore choose a provider from switzerland as your primary email.
For more information see Data protection in Switzerland and also New Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP)If you have to choose between a provider in the EU and the US, choose the one in EU, for more infomation see Additional Research section below.
-
-
Second common privacy mistake some people do is having same online profile on multiple sites, for example same username, avatar or bio on multiple forums and similar sites.
There are several reasons why this is normal, but regardless of your reasons I it’s not good for privacy because you run the risk of being stalked and also if your identity is somehow revealed you’ll be revealed in all places where you use same username or avatar and then people who are in fact not stalkers may become one, most likely someone who knows you in real life.
-
Third privacy mistake is using your real name or family name or a portion of it in username or your real picture for avatar.
Someone from your real life could easily connect the dots between your username and your online behavior and then the risk is same as with reuse of avatars and usernames mentioned before.Stalking isn’t the only issue though, it’s about your feelings or having a sense of privacy, a potential stalker might share information about you elsewhere and that’s one bad feeling to be aware of.
How do I regain trust in my computer
The question is how do I regain trust in my computer?
I installed unsigned software recently, I recall visiting potentially bad website, I recall my antivirus detected something, I was using Administrator account to go online etc. etc.
If you ask yourself such or similar questions then you can’t trust your computer and this means trust must be regained.
The only way to regain trust is to clean reload operating system, and then making sure not to repeat the mistake that led to asking these questions.
Reinstalling the system should be followed by securing it and changing all your passwords with new
ones, including router password and settings.
If your privacy was seriously compromised you should also consider creating a new online identity,
this means creating new email’s and registering new accounts, including changing your phone number
if it was used for ex. two step verification.
There is no alternative to clean reload, scanning your PC for malware is of no help since antivirus won’t detect FUD malware.
Changing your passwords on an untrusted computer is worse than not changing them at all, since if your computer isn’t trusted then how do you know your input isn’t intercepted?
Switching from Administrator account to standard account if you were Admin is beating a dead horse
since if you were Admin then your system already was online in elevated mode and is thus impossible
to be sure nothing bad happened so far.
This applies to built-in Administrator account which by default on Windows server and perhaps other
editions is not subject to UAC.
Clean reload isn’t 100% certainty though, for neither security nor privacy, security wise clean reload won’t get rid or hardware based malware if there is one, and privacy wise your computer ID’s are permanent and already stored on servers which you visit.
To also rule out this, one would have to purchase a brand new computer and even then it won’t be 100% certainty because we can’t know whether hardware manufacturer or perhaps their employee is trusted, nor can we know for certain what did people in computer shop do to the hardware.
But going that far makes not much sense, hardware malware is difficult to write and is usually used to target corporations not individual users, and preventing share of your PC ID’s can’t be prevented without also harming your comfort of computing, so buying a new computer would only create a new identity but not solve the problem.
Therefore clean reload is the most sane and economically efficient method and it gives let’s say 99% certainty.
To have 100% certainty one would have to recycle the computer, bury the remains underground and never use a computer again.
Additional research
The following web sites are good starting point for additional research regarding security and privacy